If you're looking for a material to produce Rotomolding, then choosing the correct raw material is key. Choosing the wrong raw material can compromise the product's quality or the performance of the rotomolded component.
In this article, we will discuss the ideal types of resins for rotomolding, including melt flow index, density, and more.
Let's get started!
Resin Selection
When selecting the raw material for rotomolding, the manufacturer must carefully analyze the strength, performance, and price of the resin to be used. To ensure the best result, it is important to evaluate the key characteristics of each resin.
CATEGORIES
There are three main categories of resins for raw materials used in rotomolding: thermoplastic, thermoset, and epoxy. The choice among them depends on the intended application, the production process, and the required cost.
Currently, the most widely used thermoplastic raw material for rotomolding is polyethylene, which holds 84% of the market, according to a study conducted by LyondellBasell
Polyethylene can still be divided into low-density polyethylene (LDPE) and high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which offer great benefits as they are lightweight, cost-effective, and have good corrosion resistance.
The same research also shows that polycarbonate, nylon, polyvinyl chloride, polyesters, and polypropylene cover the remaining 15% of the rotomolding market.
Resins Available in the Market
With the continuous growth of the rotomolding industry, many types of resins have emerged in the market for use as raw materials. The resins used for manufacturing rotomolded parts have a significant influence on the strength, elasticity, and vibration resistance of the finished products.
The selection of the right resin will mainly depend on the final use of the product. In any case, here are some of the main resins available in the market for rotomolding raw materials:
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE)
As mentioned earlier, high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is widely employed in rotational molding due to its remarkable chemical resistance, abrasion resistance, fungus corrosion resistance, mechanical robustness, exceptional durability, and reduced cost.
Polypropylene (PP)
PP exhibits higher stiffness compared to polyethylene, coupled with a higher thermal distortion temperature. Additionally, it has excellent ability to resist cracks caused by chemical and environmental stress. However, its impact resistance at low temperatures is lower.
Glass-Reinforced Polyester (GRP)
GRP is known as one of the most versatile resins as it offers exceptional chemical resistance, abrasion resistance, impact resistance, and fatigue resistance. It has the ability to maintain its high-performance characteristics even when exposed to extreme temperatures. However, it is a more challenging material to mold and is also more expensive.
Polycarbonate (PC)
PC is a resin that offers high transparency and rigidity but has lower impact resistance, requiring a more advanced technical process. Polycarbonate also absorbs moisture, making it less suitable for the rotomolding process.
Índice de Fusión
Raw material for rotomolding is one of the key materials in industrial processes.
Melt Flow Index (MFI) is a measure used to determine the ease with which this raw material transitions from a solid state to a liquid state. In other words, the Melt Flow Index indicates the degree to which a raw material melts, which is necessary for rotomolding.
The Melt Flow Index can be defined as 'an approximate measure of the molecular weight or chain length of a resin.' Resins with a high Melt Flow Index have shorter chains and lower molecular weight, resulting in smaller molecules. On the other hand, resins with a low Melt Flow Index have longer chains and higher molecular weight, resulting in larger molecules.
What is the ideal Melt Flow Index?
Raw materials for rotomolding should have an ideal Melt Flow Index to ensure a quality finish for the final product. There are different types of raw materials with varying Melt Flow Index values, ranging from 80°C to 273°C.
Among the best raw materials for rotomolding are plastic polymers such as PE (Polyethylene) and PP (Polypropylene). PE has an MFI between 110°C and 135°C, while PP has an MFI between 180°C and 220°C. These plastic polymers are characterized by their mechanical and weather resistance, as well as their ease of handling.
Density of Rotomolding Raw Material
Density is an important characteristic to consider when selecting raw material for rotomolding. Density is the ratio of mass to volume of a given material and is expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). The density of a material varies with temperature, pressure, and composition.
There are different materials that can be used in rotomolding, each with different densities:
Low-density resins
With values below 0.925 g/cm³, they are typically chosen when rigidity is not crucial or desired, such as in many types of toys and situations where light loads are expected.
Medium-density resins
They range from 0.926 g/cm³ to 0.940 g/cm³, with the majority of low-density polyethylene resins falling into this category. They can be used in self-supporting parts that require a higher level of resistance to thermal distortion or rigidity not offered by resins of other densities.
High-density resins
The range goes from 0.941 g/cm³ to 0.959 g/cm³ and provides greater rigidity to the developed product, allowing for a reduction in the thickness of the part's wall.
There are also very high-density resins (above 0.960 g/cm³), but they are not used in the rotomolding process.
Importance of density
Density is an important factor to consider in rotomolding raw material, as it influences mechanical strength, dimensional stability, tensile strength, and part resistance. Additionally, density affects resistance to chemicals, water absorption, and thermal conductivity.
Therefore, it is important that the material selected for rotomolding is the most suitable for the desired characteristics of the final product.
Polyethylene
Polyethylene is one of the primary raw materials for rotomolding. It is a lightweight, strong, and versatile resin, making it extremely popular for various rotomolding applications. Polyethylene is commonly used in rotomolded product designs such as containers, insulators, cubes, tanks, and boxes.
Varieties
There are many different varieties of polyethylene for rotomolding that industrial product manufacturers can choose from. High-density linear polyethylene (HDPE) is used for impact-resistant items such as boxes, while low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is used for items that require flexibility, such as hoses and flexible tanks. Cross-linked high-density polyethylene (HDPE) is used for items requiring chemical resistance, such as tanks, vessels, and containers.
Advantages
Polyethylene has many advantages over other raw materials for rotomolding. It is cheaper than other plastics as it is easier to process and manufacture.
Additionally, it is resistant to corrosion, chemicals, UV, heat, and cold, making it ideal for outdoor use. Lastly, it is a versatile material that can be molded into a variety of shapes, making it ideal for manufacturing industrial products.
Types of Polyethylene para materia prima de rotomoldeo
Polyethylene is one of the most common types of raw material for rotomolding. It is a versatile plastic raw material known for its strength and durability, making it ideal for rotomolded products. There are three main types of polyethylene: low-density polyethylene (LDPE), high-density polyethylene (HDPE), and linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE).
LDPE is a less dense and more flexible type of polyethylene, making it ideal for creating more flexible rotomolded products. On the other hand, HDPE is denser and therefore stronger. Lastly, LLDPE is the toughest type of polyethylene, making it ideal for manufacturing products that require higher strength and durability.
Additionally, it is important to consider other properties of the polyethylene types, such as impact resistance, moisture resistance, temperature resistance, and chemical resistance. Choosing the ideal type of raw material for rotomolding is essential to produce high-quality products that meet market demands.
Polyethylene Pellets
Pellets are the previous stage of polyethylene used in the rotational molding process. This is because the pellets need to be micronized and reduced to much smaller particles, which improves the flow of these particles during the melting of polyethylene.
Polyethylene Resins: Advantages and Disadvantages
Polyethylene resins are the most common and affordable raw material for rotomolding.
Advantages
These resins are extremely versatile, easily adapting to various needs in packaging, recreation, pool heating, and other applications. This resin has low density and compliance at low temperatures while maintaining its strength and impermeability.
Disadvantages
The most obvious disadvantage of polyethylene resins is the possibility of shrinkage, which can lead to deformation of the piece. Polyethylene resins also have higher susceptibility to UV radiation, resulting in greater fragility during exposure to this radiation. However, this can be addressed through the use of additives.
In summary, here are some reasons for using polyethylene in rotomolding:
- Easily ground to 35 mesh at high rates.
- Can be thermally stable with appropriate stabilization additives.
- Possess excellent physical properties at low temperatures, such as impact resistance, allowing for a wide temperature range of use.
- Relatively low cost.
- Available in a wide range of densities and melt flow indices to meet the needs of simple and non-stressed items.
- UV stability or outdoor life can be significantly improved by the addition of pigments or UV stabilizers.
- Excellent chemical resistance, making them ideal for various large agricultural and industrial chemical tanks.
Other Rotomolding Resins
The main advantages of using resins as raw material for rotational molding are the higher strength, durability, and better finish of the final products.
Various resins can be employed in the production of parts by rotational molding, in addition to polyethylene.
One alternative is polyurethane. This material is resistant and highly flexible, allowing for the production of end products with great strength and durability.
Another alternative for rotomolding raw material is epoxy resin. This resin is easy to handle, coats and fills well, and has superior chemical resistance, making it ideal for use in harsh environments.
Below is a comparative table of these and other resins available in the market:
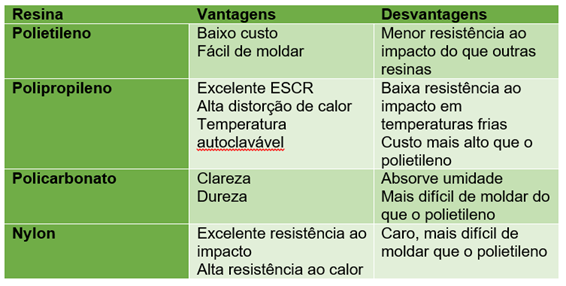
Conclusion
In conclusion, it can be said that choosing the right resin is essential to achieve good results in rotomolding. The right raw material ensures that the final product is of high quality and meets consumer expectations.
With knowledge of the advantages and disadvantages of the main resins in the market, it becomes much easier to find the best option for part production. However, it is important to keep in mind that the melt index and density of a resin can vary depending on the type of polymer used in its formulation.
Therefore, considering all the aspects covered in this article, it becomes possible to choose the ideal raw material for rotational molding, resulting in impressively high-quality rotomolded products.